Securing attributes are used by Oracle
HTML-based applications to allow rows (records) of data to be visible
to specified users or responsibilities based on the specific data
(attribute values) contained in the row. You may assign one or more
values for any of the securing attributes assigned to the user. If a
securing attribute is assigned to both a responsibility and to a user,
but the user does not have a value for that securing attribute, no
information is returned for that attribute.

For example, to
allow a user in the ADMIN responsibility to see rows containing a
CUSTOMER_ID value of 1000, assign the securing attribute of CUSTOMER_ID
to the ADMIN responsibility. Then give the user a security attribute
CUSTOMER_ID value of 1000.
When the user logs into the Admin responsibility, the only customer data they have access to has a CUSTOMER_ID value of 1000.
Fields
Attribute
: Select an attribute you want used to determine which records this
user can access. You can select from any of the attributes assigned to
the user's responsibility.
Value : Enter the value for the attribute you want used to determine which records this user can access.
Creation of Responsibility
Navigation – System Administrator ->Security -> Responsibility -> Define
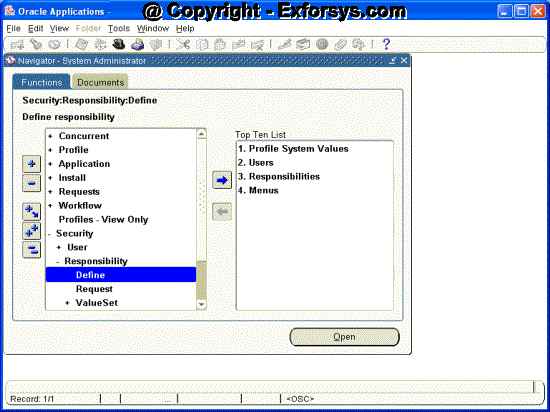
Figure 5. Create Responsibility Navigation
Follow the above the navigation path and click on Define. You will see following screen in front of you.
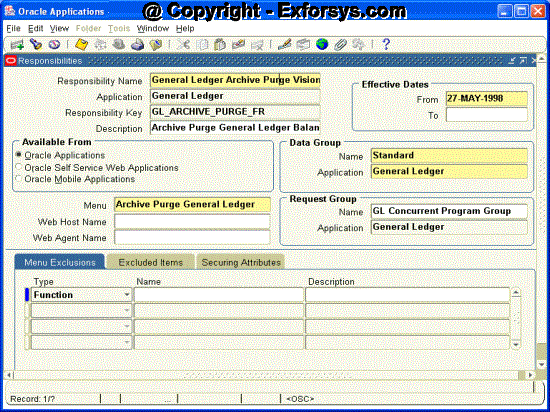
Fields
Responsibility Name - If you have multiple responsibilities, a pop-up window includes this name after you sign on.Application - This

Responsibility Key - This is a unique name for a responsibility that is used by loader programs. Loaders are concurrent programs used to "load" such information as messages, user profiles and user profile values into your Oracle Applications tables. To help ensure that your responsibility key is unique throughout your system, begin each Responsibility Key name with the application short name associated with this responsibility.
Effective Dates From/To - Enter the start/end dates on which the responsibility becomes active/inactive. The default value for the start date is the current date, and if you do not enter an end date, the responsibility is valid indefinitely.
You cannot delete a responsibility because its information helps to provide an audit trail. You can deactivate a responsibility at any time by setting the end date to the current date. If you wish to reactivate the responsibility, change the end date to a date after the current date, or clear the end date.
Available From - A responsibility may be associated with only one applications system. Select between Oracle Self-Service Web Applications or Oracle Applications.
Data Group - Name/Application The data group defines the pairing of application and ORACLE username. Select the application whose ORACLE username forms connect to when you choose this responsibility. The ORACLE username determines the database tables and table privileges accessible by your responsibility. Transaction managers can only process requests from responsibilities assigned the same data group as the transaction manager.
Menu - The menu whose name you enter must already be defined with Oracle Applications.
Web Host Name - If your Web Server resides on a different machine from your database, you must designate the host name (URL) here. Otherwise, the Web Host Name defaults to the current database host server.
Web Agent Name - Enter the PL/SQL Agent Name for the database used by this responsibility. If you do not specify an Agent Name, the responsibility defaults to the agent name current at log-on.
Request Group Name/Application - If you do not assign a request security group to this responsibility, a user with this responsibility cannot run requests, request sets, or concurrent programs from the Submit Requests window, except for request sets owned by the user. The user can access requests from a Submit Requests window you customize with a request group code through menu parameters.
Menu Exclusions Block
Define function and menu exclusion rules to restrict the application functionality accessible to a responsibility.Type : Select either Function or Menu as the type of exclusion rule to apply against this responsibility.
-
When you exclude a function from a responsibility, all occurrences of that function throughout the responsibility's menu structure are excluded.
-
When you exclude a menu, all of its menu entries, that is, all the functions and menus of functions that it selects are excluded.
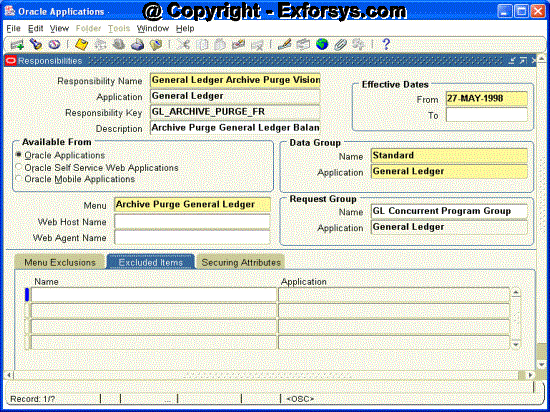
Figure 7. Create Responsibility Excluded Items
Excluded Items : Use the List of Values to select valid attributes. You can assign any number of Excluded Attributes to a responsibility
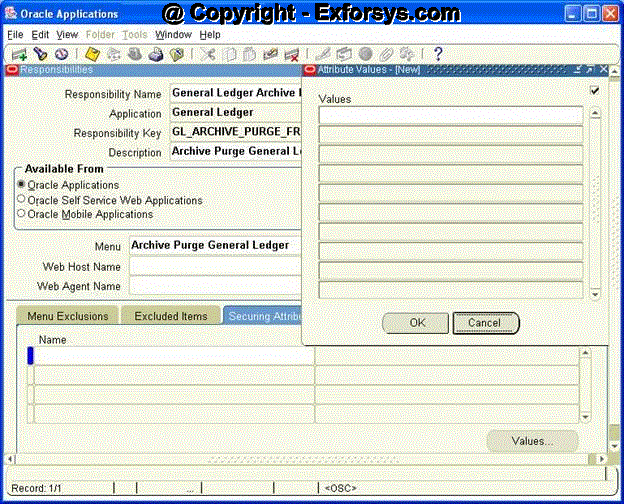
Figure 8. Create Responsibility Securing Attributes
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the significance of securing attributes while creating users?2. What is the significance of securing attributes while creating responsibilities?
3. What is the significance of Menu Exclusions in responsibility?
4. What is Excluded Items in Responsibility?
5. How do I assign a responsibility to a user?
6. What is data group in a responsibility?
7. What is the significance of Request Group in the responsibility?

No comments:
Post a Comment